Medical Dermatology
Why see a board-certified dermatologist?
Board Certified Dermatologists have completed four years of medical school followed by four years of advanced medical training in dermatology. They are experts in the treatment of more than 3,000 conditions that affect the skin, hair, and nails. Skin diseases are especially common, affecting one in four Americans each year.
What does FAAD stand for?
Fellow of the American Academy of Dermatology
Why choose a FAAD dermatologist?
You will receive medical care from a doctor who has the most rigorous medical education and training to diagnose and treat more than 3,000 skin, hair, and nail conditions
They are board-certified in dermatology, having passed the rigorous board exams given by the American Board of Dermatology, the American Osteopathic Board of Dermatology, or the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada.
They keep up with medical advancements and continue to enrich their medical knowledge.
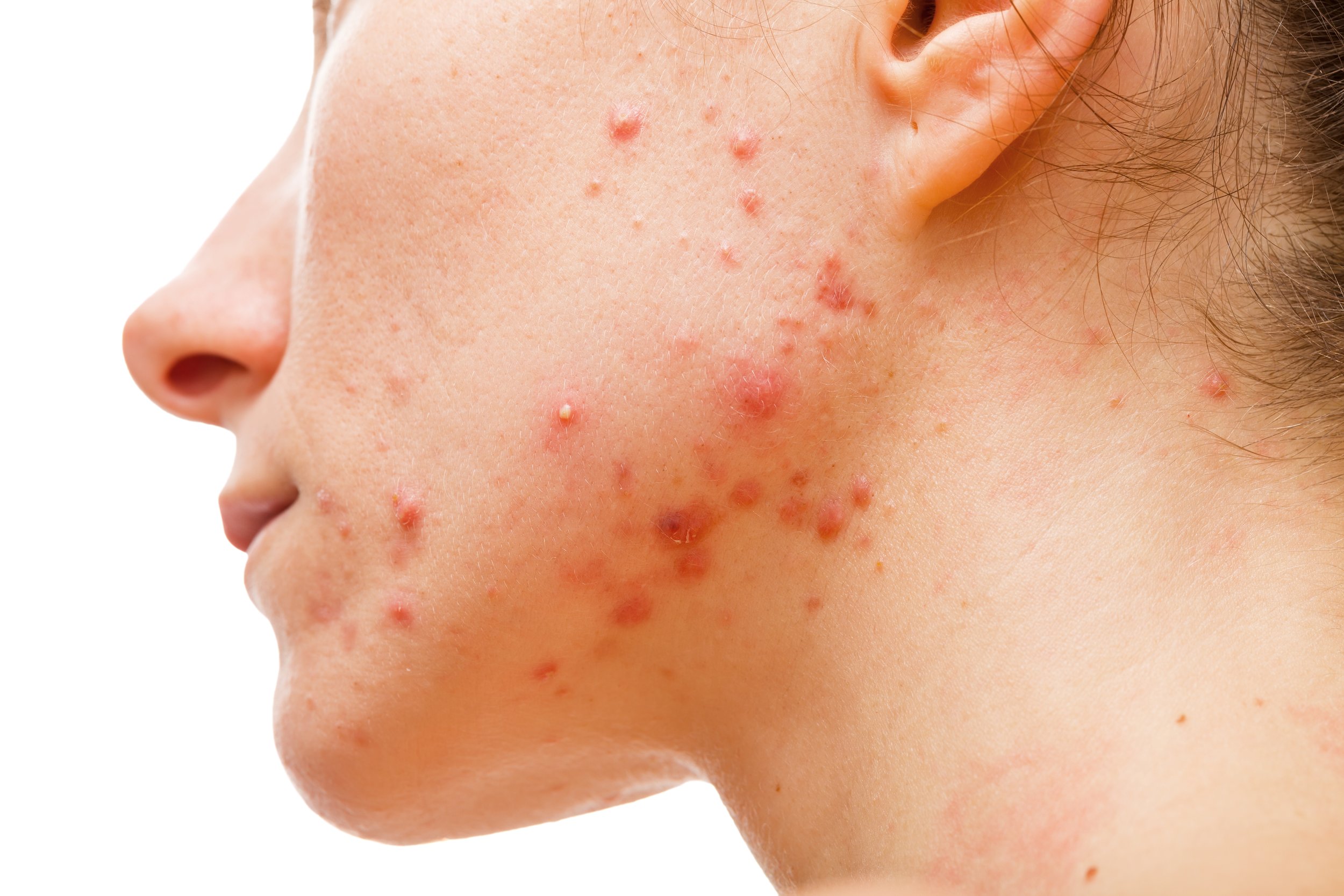
Acne
Acne is a common chronic disorder affecting the hair follicle and sebaceous gland, in which there is expansion, blockage, and inflammation surrounding the follicle. Acne affects males and females of all races and ethnicities. It is prevalent in adolescents and young adults. However, it may sometimes occur in children and adults of all ages.
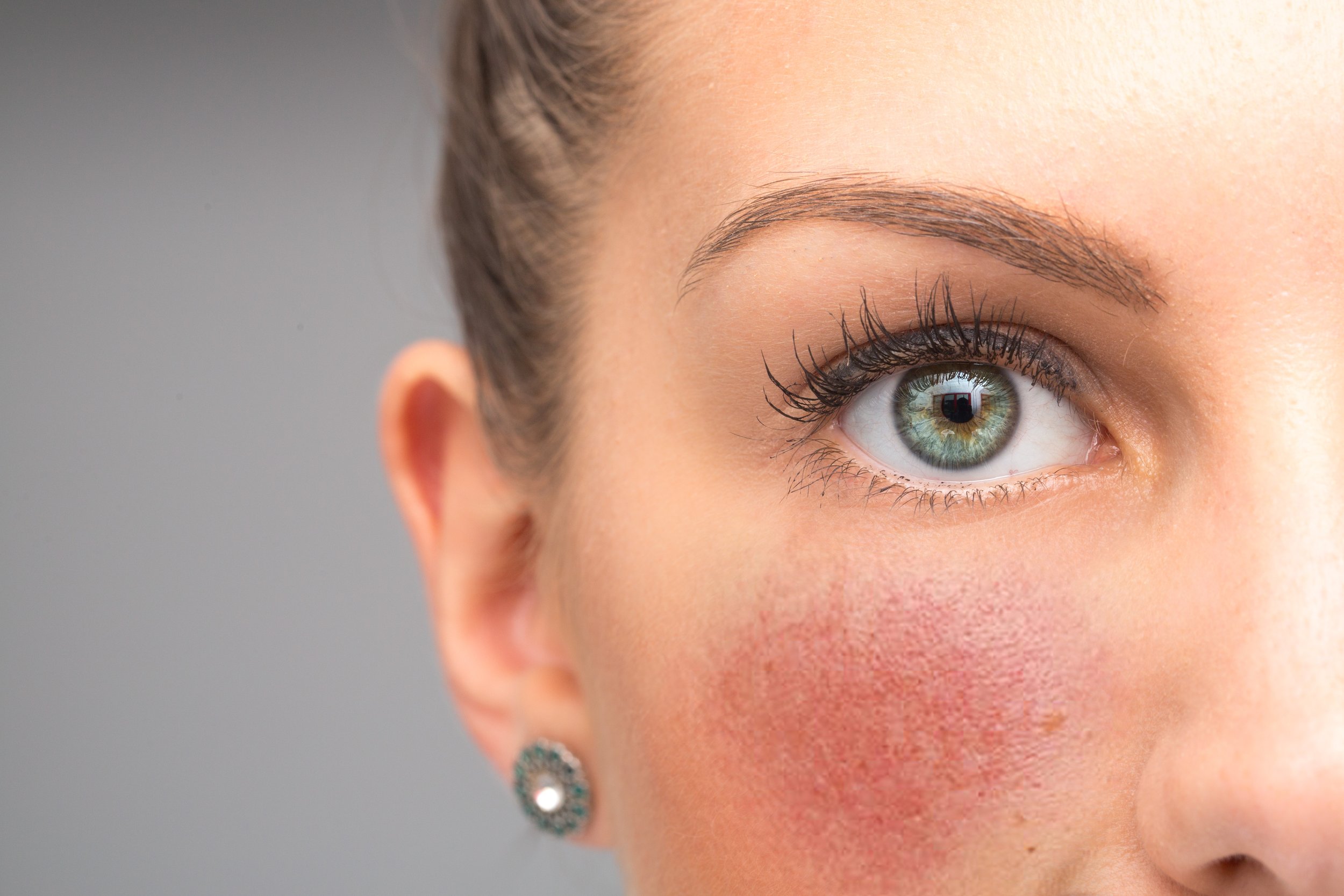

Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic rash involving the central face that most often starts between the age of 30 and 60 years. It may be transient, recurrent, or persistent and is characterized by its color, red.
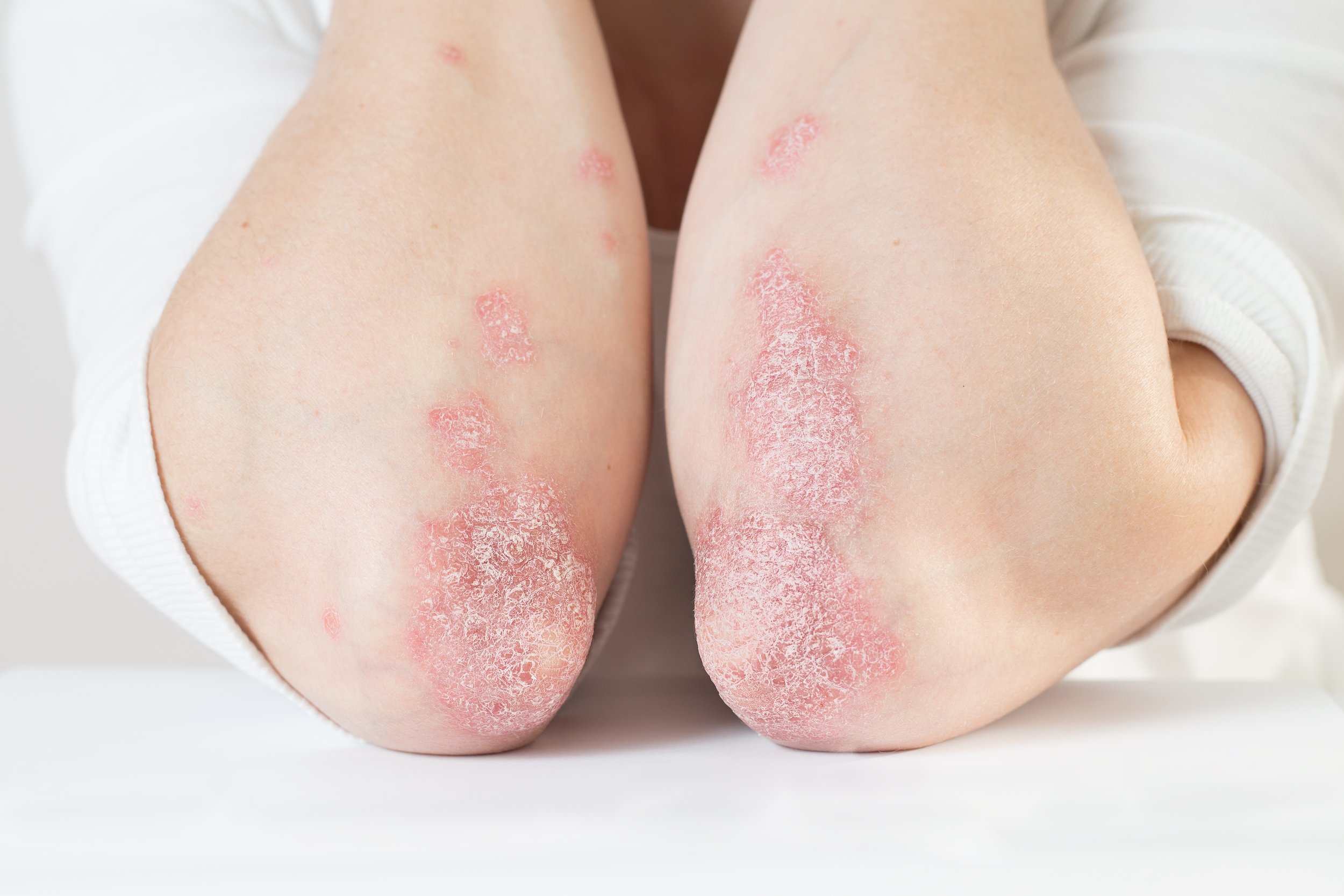
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by clearly defined, red, and scaly plaques (thickened skin). It is classified into several subtypes. Psoriasis is multifactorial. It is classified as an immune-mediated inflammatory disease (IMID). The most common sites are scalp, elbows, and knees, but any part of the skin can be involved including nails.
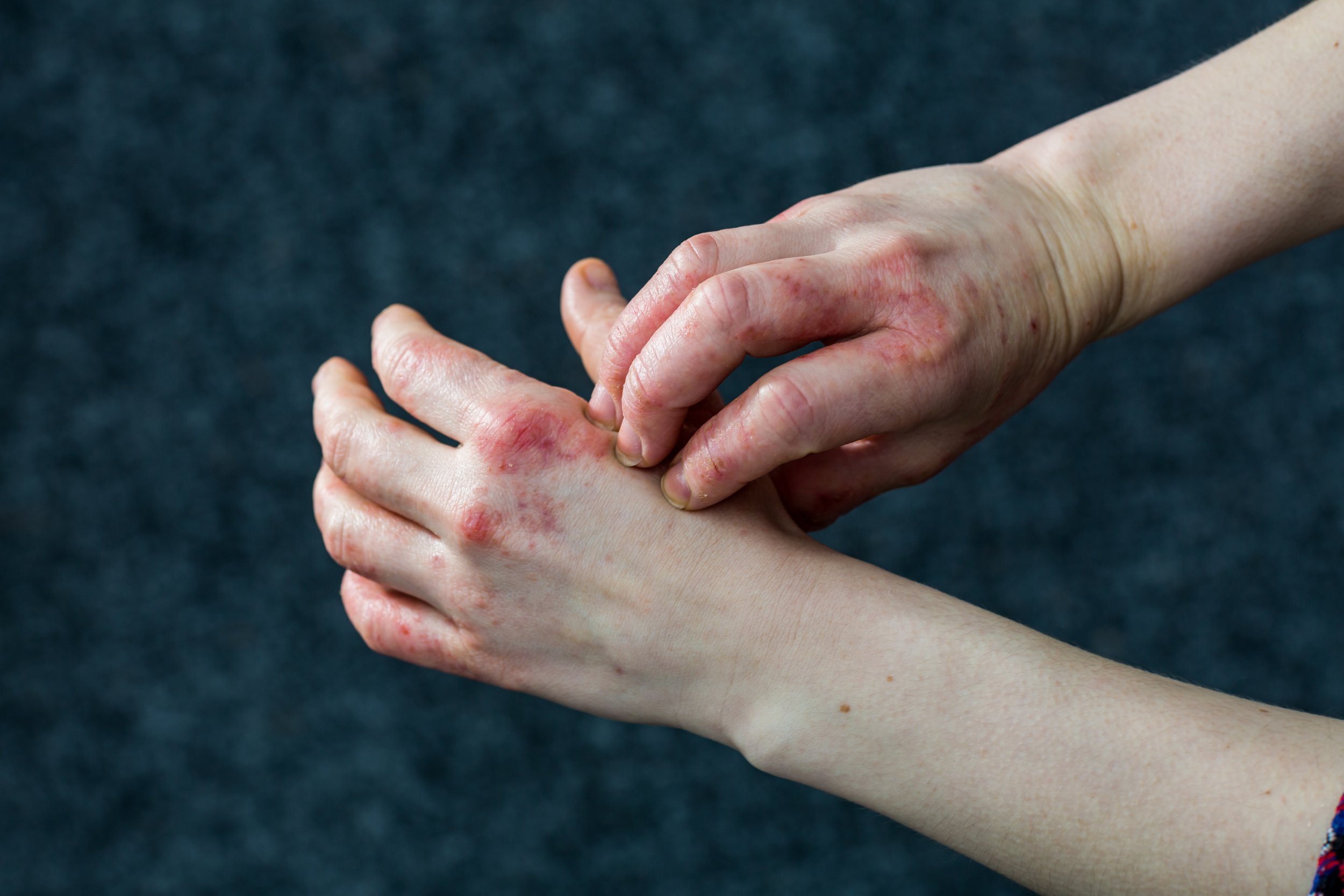
Eczema
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic, itchy skin condition that is very common in children but may occur at any age. Atopic dermatitis usually occurs in people who have an 'atopic tendency'. This means they may develop any or all of three closely linked conditions; atopic dermatitis, asthma and hay fever (allergic rhinitis). Often, these conditions run within families with a parent, child or sibling also affected. A family history of asthma, eczema, or hay fever is particularly useful in diagnosing atopic dermatitis in infants.
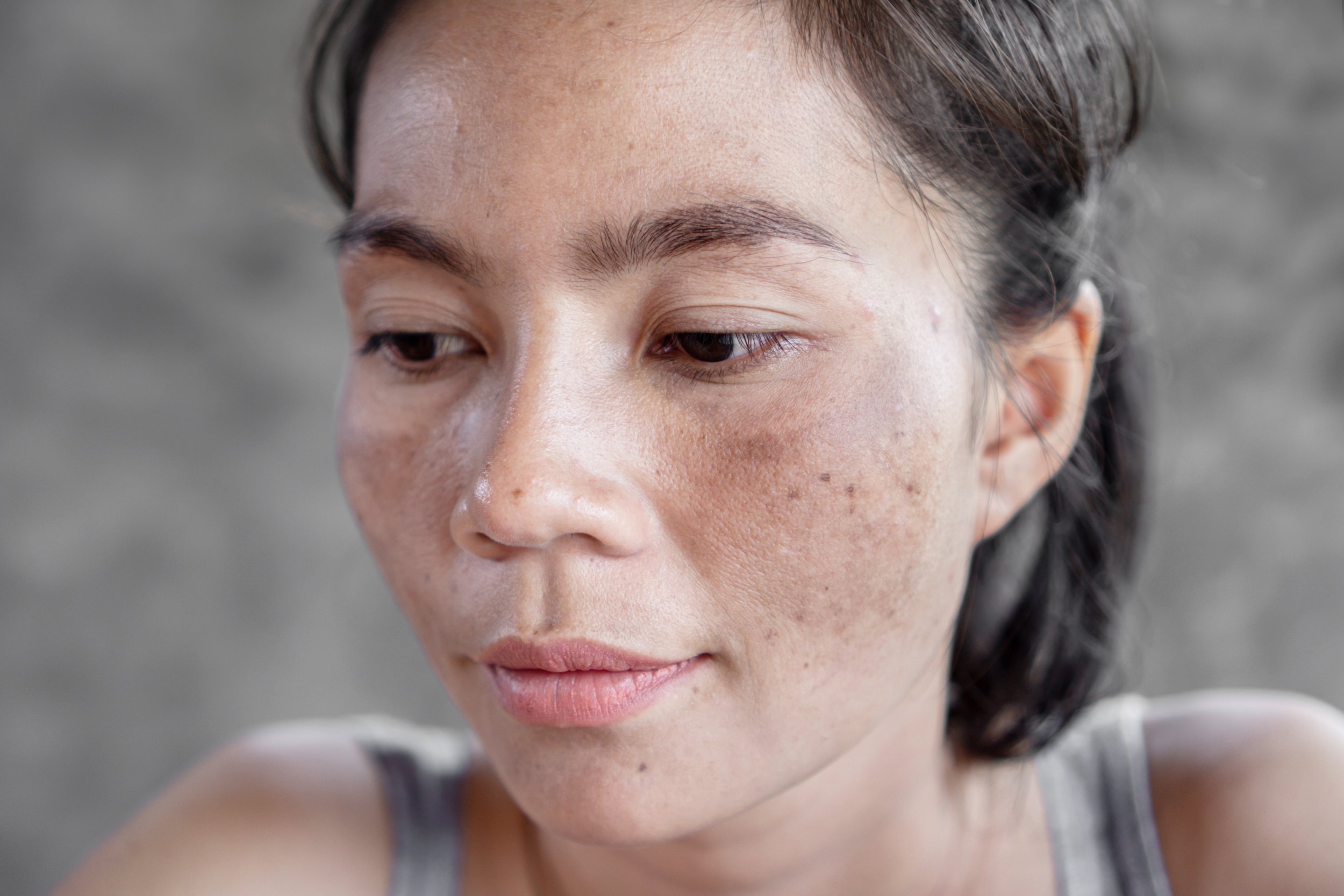

Melasma
Melasma is a chronic skin disorder that results in symmetrical, blotchy, and brownish facial pigmentation. Melasma can also affect the arms and back. It can lead to considerable distress.
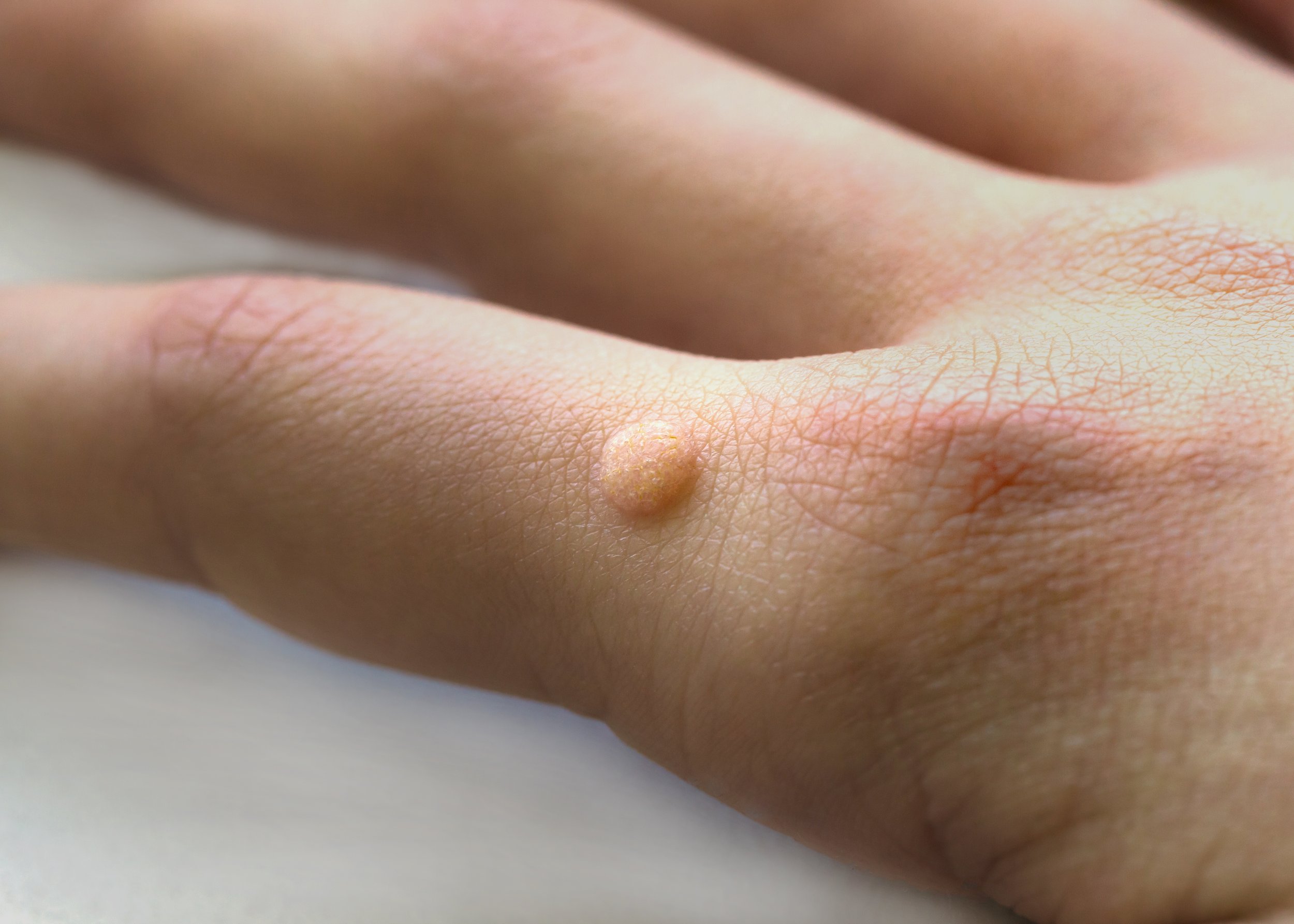
Warts
A viral wart is a very common growth of the skin caused by infection with human papillomavirus (HPV). Warts are particularly common in school-aged children, but they may arise at any age, in people with eczematous skin due to a defective skin barrier, and in people who are immune-suppressed with medications.

Skin Cancer Evaluation
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States, with millions of cases diagnosed each year. It is also one of the most preventable cancers and highly treatable when detected early. Read below to find dermatologists' expertise to help you prevent and find skin cancer, along with information to help you make informed treatment decisions.
-
BCC is most common in people who have fair skin, but people of all colors get this skin cancer. For most people, BCC is not life-threatening. It tends to grow slowly. It seldom spreads to another part of the body. Even so, treatment is important. Given time to grow, this skin cancer can grow deep, injuring nerves, blood vessels, and anything else in its path. As the cancer cells pile up and form a large tumor, the cancer can reach into the bone beneath. This can change the way you look, and for some people the change may be disfiguring.
-
Squamous cells are found throughout the human body. These cells line organs, such as the lungs, throat, and thyroid. We also have squamous cells in our skin.
Anywhere we have squamous cells, we can develop a type of cancer called squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). In the skin, this cancer is usually not life-threatening. It tends to grow slowly, but it can grow deep. When the cancer grows deep, it can injure nerves, blood vessels, and anything else in its path. As the cancer cells pile up, a large tumor can form. Before developing this skin cancer, people tend to notice signs of sun damage on their skin, such as age spots, patches of discolored skin, and deep wrinkles.
-
Melanoma is often called the “most serious skin cancer” because it can spread from the skin to other parts of the body. Melanoma is a skin cancer that can show up on the skin in many ways. It can look like:
a changing mole
a spot that looks like a new mole, freckle, or age spot, but it looks different from the others on your skin
a spot that has a jagged border, more than one color, and is growing
a band of darker skin around a fingernail or toenail
-
Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
Sebaceous cell carcinoma
